概述
什么是hibernate?
Hibernate框架是当今主流的Java持久化框架之一,由于具有简单易学、灵活性强、扩展性强等特点,能够大大地简化程序地代码量,提高工作效率。
hibernate是一个开放源代码地ORM框架,它对JDBC进行了轻量级地对象封装,使得Java开发人员可以使用面向对象地编程思想来操作数据库。
ORM:Object Relational Mapping对象关系映射
特点
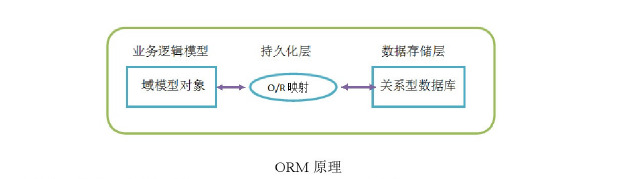
所谓地ORM就是利用描述对象和数据库表之间映射地元数据,自动把Java应用程序中地对象,持久化到关系型数据库地表中。通过操作Java对象,就可以完成数据库表地操作。可以把ORM理解为关系型数据和对象地一个纽带,开发人员只需要关注纽带一端地映射地对象即可。ORM原理如下图:
优势:
- hibernate对JDBC访问数据库地代码做了轻量级封装,大大简化了数据访问层繁琐地重复性代码,并且减少了内存消耗,加快了运行效率
- hibernate是一个基于JDBC的主流持久化框架,是一个优秀地ORM实现,它很大程度地简化了DAO层编码工作
- hibernate地性能非常好,映射地灵活性很出色,它支持很多关系型数据库,从一对一到多对多地各种复杂关系
- 可扩展性强,由于源代码地开源以及API的开放,当本身功能不够用时,可以自行编码进行扩展
hibernate的入门
下载
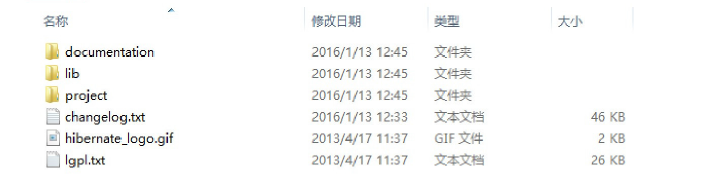
解压后的目录结构如下:
- document文件夹:存放hibernate的相关文档,包含参考文档的API文档
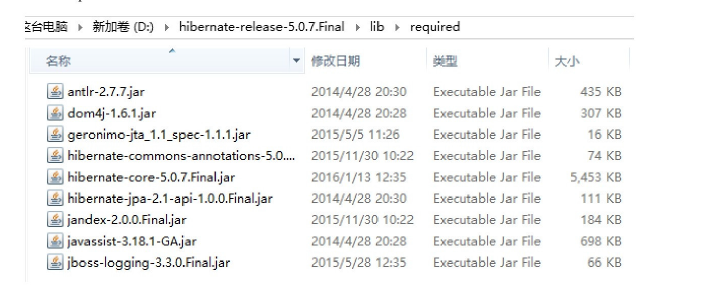
- lib文件夹:存放hibernate编译和运行所依赖的jar包。其中required子目录下包含了运行hibernate5项目所必须的jar包
- project文件夹:包含的jar包
在lib/required子目录中包含的jar包:
框架搭建
-
创建数据库
CREATE TABLE `cst_customer` ( `cust_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '客户编号(主键)', `cust_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '客户名称(公司名称)', `cust_user_id` bigint(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '负责人id', `cust_create_id` bigint(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建人id', `cust_source` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户信息来源', `cust_industry` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户所属行业', `cust_level` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户级别', `cust_linkman` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人', `cust_phone` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '固定电话', `cust_mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '移动电话', PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -
书写ORM元数据(对象与表的映射配置文件)idea自动生成
package com.hibernate.domain; import javax.persistence.*; import java.util.Objects; @Entity @Table(name = "cst_customer", schema = "yy-visualization", catalog = "") public class CstCustomerEntity { private long custId; private String custName; private Long custUserId; private Long custCreateId; private String custSource; private String custIndustry; private String custLevel; private String custLinkman; private String custPhone; private String custMobile; @Id @Column(name = "cust_id") public long getCustId() { return custId; } public void setCustId(long custId) { this.custId = custId; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_name") public String getCustName() { return custName; } public void setCustName(String custName) { this.custName = custName; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_user_id") public Long getCustUserId() { return custUserId; } public void setCustUserId(Long custUserId) { this.custUserId = custUserId; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_create_id") public Long getCustCreateId() { return custCreateId; } public void setCustCreateId(Long custCreateId) { this.custCreateId = custCreateId; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_source") public String getCustSource() { return custSource; } public void setCustSource(String custSource) { this.custSource = custSource; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_industry") public String getCustIndustry() { return custIndustry; } public void setCustIndustry(String custIndustry) { this.custIndustry = custIndustry; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_level") public String getCustLevel() { return custLevel; } public void setCustLevel(String custLevel) { this.custLevel = custLevel; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_linkman") public String getCustLinkman() { return custLinkman; } public void setCustLinkman(String custLinkman) { this.custLinkman = custLinkman; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_phone") public String getCustPhone() { return custPhone; } public void setCustPhone(String custPhone) { this.custPhone = custPhone; } @Basic @Column(name = "cust_mobile") public String getCustMobile() { return custMobile; } public void setCustMobile(String custMobile) { this.custMobile = custMobile; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; CstCustomerEntity that = (CstCustomerEntity) o; return custId == that.custId && Objects.equals(custName, that.custName) && Objects.equals(custUserId, that.custUserId) && Objects.equals(custCreateId, that.custCreateId) && Objects.equals(custSource, that.custSource) && Objects.equals(custIndustry, that.custIndustry) && Objects.equals(custLevel, that.custLevel) && Objects.equals(custLinkman, that.custLinkman) && Objects.equals(custPhone, that.custPhone) && Objects.equals(custMobile, that.custMobile); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(custId, custName, custUserId, custCreateId, custSource, custIndustry, custLevel, custLinkman, custPhone, custMobile); } }<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 配置表与实体对象的关系--> <hibernate-mapping> <!-- package属性:填写一个包名,在元素内部凡是需要完整类名的属性可以直接写类名 --> <class name="com.hibernate.domain.CstCustomerEntity" table="cst_customer" schema="yy-visualization"> <!-- class元素:配置实体与表的对象关系 name:完整类名 table:数据库表名 --> <id name="custId" column="cust_id"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <!-- id元素:配置逐渐映射属性 name:填写主键对应属性名 column:填写表中的逐渐列名 generator:逐渐生成策略 --> <property name="custName" column="cust_name"/> <property name="custUserId" column="cust_user_id"/> <property name="custCreateId" column="cust_create_id"/> <property name="custSource" column="cust_source"/> <property name="custIndustry" column="cust_industry"/> <property name="custLevel" column="cust_level"/> <property name="custLinkman" column="cust_linkman"/> <property name="custPhone" column="cust_phone"/> <property name="custMobile" column="cust_mobile"/> <!-- property元素:配置逐渐映射属性 name:填写除主键外对应属性名 column(可选):填写表中的列名,默认值:列明会使用默认属性 type(可选):填写列的类型,如果不填hibernate会自动检测实体的属性类型。每个类型有三种:Java类型|hibernate类型|数据库类型 not-null(可选):配置该属性是否不能为空,默认值:false length(可选):配置数据库中列的长度,默认值:当前数据库类型的最大长度 --> </class> </hibernate-mapping> -
书写主配置文件
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 如果出现中文乱码则将url改为:jdbc:mysql://113.141.72.49:3306/yy-visualization?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8--> <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://113.141.72.49:3306/yy-visualization</property> <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">root</property> <!--配置数据库方言:在不同的数据库中,不同的sql语法有区别,指定方言可以让hibernate框架在生成sql语句时,针对数据库的方言生成--> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect</property> <!--显示sql --> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <!--格式化sql --> <property name="format_sql">true</property> <!-- 指定自动生成数据表的策略 --> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- auto schema export 自动导数表结构,自动建表 hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop 自动建表,每次框架运行结束都会将所有表删除(开发测试中使用) create 自动建表,每次框架运行完之后都会创建新表,表数据会丢失(开发测试中使用) update(推荐使用) 自动建表,如果已经存在不会再生成,如果表有变动,自动更新表 validate 校验,不自动生成表。每次启动会校验数据库中表是否正确,校验失败,抛异常 --> <mapping resource="com/hibernate/domain/CstCustomerEntity.hbm.xml"/> <mapping class="com.hibernate.domain.CstCustomerEntity"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration> -
测试代码
package com.hibernate.test; import com.hibernate.domain.CstCustomerEntity; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.junit.Test; //测试类 public class Demo { @Test public void fun1() { //保存客户 Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); //书写业务代码 CstCustomerEntity c=new CstCustomerEntity(); c.setCustName("百度"); session.save(c); transaction.commit(); session.close(); sessionFactory.close(); } }
API详解
Configuration
功能:配置文件加载类,用于加载主配置,orm元数据加载
-
创建
Configuration configuration = new Configuration() -
读取指定配置文件
configuration.configure();//有五个重载方法 /** 空参的方法,默认加载名为hibernate.cfg.xml文件 public Configuration configure() throws HibernateException { return this.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml"); } public Configuration configure(String resource) throws HibernateException { this.standardServiceRegistryBuilder.configure(resource); this.properties.putAll(this.standardServiceRegistryBuilder.getSettings()); return this; } public Configuration configure(URL url) throws HibernateException { this.standardServiceRegistryBuilder.configure(url); this.properties.putAll(this.standardServiceRegistryBuilder.getSettings()); return this; } public Configuration configure(File configFile) throws HibernateException { this.standardServiceRegistryBuilder.configure(configFile); this.properties.putAll(this.standardServiceRegistryBuilder.getSettings()); return this; } @Deprecated public Configuration configure(Document document) throws HibernateException { return this; } **/ -
根据配置消息,创建SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
SessionFactory
功能:用于创建操作数据库核心对象session对象的工厂。简而言之,就是创建session
注意:
- SessionFactor用于保存和使用所有的配置信息,消耗内存资源非常大
- SessionFactory属于线程安全的对象设计
结论:保证web项目中,只创建一个SessionFactory
Session
session是应用程序与数据库之间交互操作的要给单线程对象,是hibernate运作的中心,他的主要功能是为持久化对象提供创建、读取、删除能力,所有持久化对象必须在session的管理下才能进行持久化操作
获得session
session.openSession();//打开一个新的session对象,在使用完后需要调用close方法手动关闭
session.getCurrentSession()//获得一个与线程绑定的session对象,在提交或者回滚操作时会自动关闭
session是线程不安全的
session中常用的方法:
- save()、update()、saveOrUpdate():用于增加和修改对象
- delete()方法:用于删除对象
- get()和load():根据主键查询
- createQuery()和createSQLQuery():用于数据库操作对象
- createCriteria():条件查询
Transaction
Transaction接口是一个可选的API,是对实际事务实现的一个抽象,这些实现包括JDBC事务等
功能:主要用于管理事务,是hibernate的数据库事务接口,且对事物的底层接口进行了封装。
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
事务管理的常用方法:
- commit():提交相关联的session实例
- rollback():撤销事务操作
sessioin执行完数据库操作之后,要使用Transaction的commit方法进行提交,才能真正的将数据库操作同步到数据库中